As promised in my previous article, I will be discussing some of my favourite marketing models that are not only a staple in marketing books but have proved to be very useful for marketing people over the years.
I am a huge fan of using marketing models. They provide a great starting point and a useful, simple framework that allows the researcher to assess not only how well a company is doing but also their competitors and allow you to plan your future strategies.
In 2011 the Chartered Institute of Marketing created a poll to celebrate 100 years of marketing and ran a live poll for their members to find out which marketing model was the most valuable one. The results of that poll were:
The top two are no surprise to me and if I had to choose my favourite model it would be the ‘Marketing Mix’, commonly referred to as ‘4/7 Ps’.
Marketing Mix Model – 4 or 7 Ps
My winner of the poll is the marketing mix. It is a model that includes the vital points in determining your marketing strategy. Marketing mix was first introduced by Jerome McCarthy in 1960 and as the results of the CIM poll prove it is still going strong today!
The marketing mix includes all the variables a business carries out its marketing strategy and provides a recipe for effective marketing.
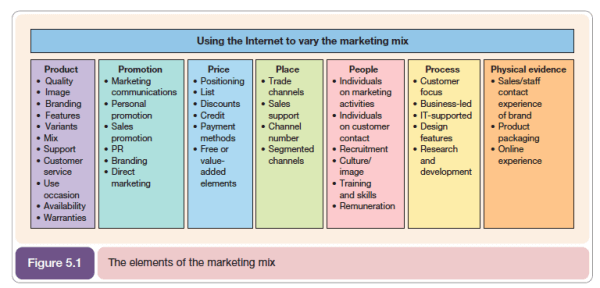
The model consists of 4 or 7 factors: product, promotion, price, place, people, process, and physical evidence. You can probably tell why it is commonly referred to as 4 or 7 Ps!
If your business only sells products, the first four Ps from the list will be of interest and if your business provides a service you will need to consider all of the 7 Ps.
The points below each ‘P’ needs to be considered when creating your marketing mix and most importantly your marketing mix needs to be consistent.
Product or Service
This includes what you offer your customers to satisfy their needs. It could be a product or a service. The series of questions you’d need to ask yourself are:
– What does your customer expect and want from your products or services? Which need of your customer does your product or service need to satisfy?
– What specialities or features does your product or service provide to meet those needs of your customers? Have you missed out anything? Do you have any costly features that aren’t necessary?
– How is your product branded?
– What support do you offer your customers?
– What is your product most used for?
– What size or colour is your product?
– What is the unique selling point (USP) of your product or service?
– Would additional products improve or add value to your offering?
– Is the product profitable?
– What is the future for the product?
Price
Your pricing strategy is another important point. You need to consider the following vital points:
– How much is your product?
– Who is it sold to?
– What is the value to the buyer?
– Can you make any adjustments to increase profit?
– Are there industry set prices?
– What affects your pricing policy?
– Are your customers price sensitive?
– How does your pricing compare to your competitors?
– Do you offer discounts? Do you need to offer discount?
– Can you gain extra market share by lowering your prices?
Promotion
Even if you have the best product in the world, without promotion no one will buy it. To attract the right people, in the right time you need to ensure you carry out promotional activity otherwise your competitors will always be stronger than you.
– Are you reaching your target market?
– What is the best way of reaching your target market? E.g. TV, radio, internet, or billboards?
– What is the best time to promote or best season?
– Are you using the most effective promotional activity?
– Which method of promotion is reaching more customers?
– Are there new methods that you could try?
– How are your competitors promoting their products?
Place
This is your distribution strategy. Where and how your customers will expect to find your products:
– Where do buyers look for your products or services?
– Are your products easily available?
– Are you selling directly to your customers?
– Do you have sufficient quantities available?
– What are the right distribution channels for your products?
– How can you access the right distribution channels?
– What channels are your competitors using?
– Are there any alternatives that are more cost effective?
These 4 Ps are the main components of this tool and most important factor whether you’re business who sells a product or a service. The following Ps are mainly for services.
People
Services rely highly on people who provide them so ‘people’ in a services marketing mix is very important.
– How selective are you when you choose people to provide your service?
– Do you offer adequate training?
– Are they aware of your business culture?
– Have you provided your people with the necessary tools to provide the service sufficiently?
– Are they well mannered?
– How satisfied are your customers by the service they receive?
– Do you motivate your people enough to want to provide an excellent service?
– Are your people presented in a way that reflects you well as a business?
Process
Process covers how your customers are handled from the moment your service starts until the very last point of contact.
– Are you providing and efficient and speedy service?
– Are you able to meet demand at peak periods?
– Can you maintain the same level of service throughout the year? At every branch? In every country?
– How are your competitors’ processes?
– What changes can you make to be more efficient?
– How do you monitor the service you provide?
Physical Evidence
This is the last P in the mix. It is essentially packaging for your service provider such as uniforms – if your service is provided by people.
– Does your décor reflect your brand?
– What is the ambience like?
– What is your premise layout like?
– Is there anything unique about your building or location?
– Could you make a change to your décor to make it unique and memorable?
– Can you offer anything to your customer to take away with them?
Using the Marketing Mix
You can use the marketing mix model to decide how to take a new offer to market or you can use it to test your existing marketing strategy. Using the marketing mix is easy, just follow these simple steps:
- Identify the product or service you want to test or analyse
- Answer the questions for each of the relevant Ps
- Once you have defined your marketing mix test it from the customer’s perspective.
- Don’t forget to review your marketing mix regularly.
Check this video out for a quick explanation of the model.
In my next article I will explaining another useful marketing model.